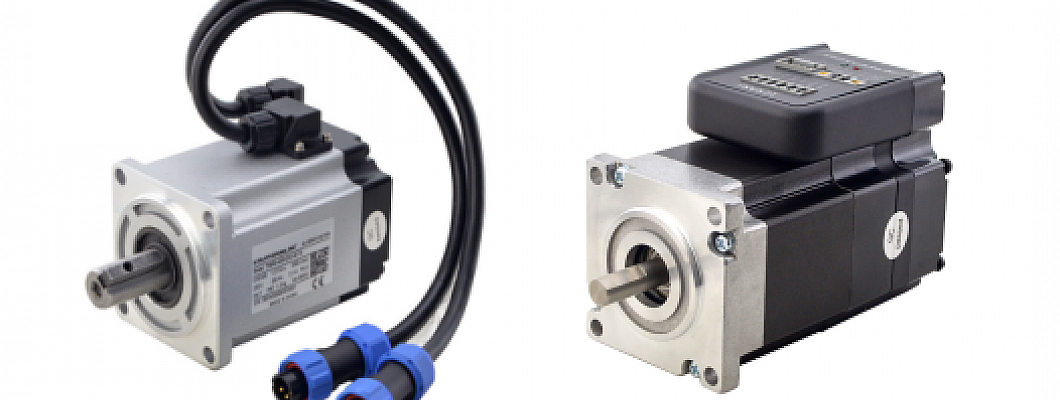
AC servo motor and DC servo motor are two types of servo motors. In this article, we'll briefly cover some of the main differences between AC and DC servo motors and their respective advantages and disadvantages, but let's start with some basics.
DC servo motor
1. Classification
DC servo motors are divided into brushed and brushless servo motors. Brushed DC servo motor - the motor has low cost, simple structure, large starting torque, wide speed range, easy control, requires maintenance (replacement of carbon brushes), will generate electromagnetic interference, and has requirements for the environment. Brushless DC servo motor - the motor is small in size, light in weight, large in output, fast in response, high in speed, small in inertia, stable in torque, easy to be intelligent, and its electronic commutation method is flexible. The motor is maintenance-free and has no loss of carbon brushes. It has high efficiency, low operating temperature, low noise, low electromagnetic radiation, and long life. It can be used in various environments. In a DC servo motor, there is a direct current (DC) with positive and negative terminals. Between each of these terminals, current flows in exactly the same direction. The brushes inside the motor need to be replaced periodically. However, the life of these brushes can be extended with regular maintenance. For DC servo motors, current control is much simpler than for AC servo motors.2. Application
DC servo motors are often used in applications that require precise control without connection to an AC power source. For example: robotic arms, AGV wheels, industrial automation equipment, printers, indexers and anything that needs to perform tasks accurately and precisely.AC servo motor
1. Classification
The two main types of AC servo motors are synchronous motors and induction motors. An induction AC motor is an asynchronous motor whose speed is related to the frequency of the corresponding current. It is the most widely used motor in everyday equipment. Synchronous AC servo motors use permanent magnets and produce rated torque at precise synchronous speeds. Its rotor speed is related to the stator because both rotate synchronously. Synchronous AC motors are also key active components in drill presses and other high-precision tools. In addition, AC servo motors can also be divided into two types: 2-phase and 3-phase AC servo motors. Most AC servo motors are two-phase squirrel-cage induction motors. They are used in low power applications. Three phase squirrel cage induction motors are now used in applications requiring high power systems. In an AC servo motor, alternating current (AC) operates in reverse order. Every second, the current alternates countless times. AC servo motors can handle varying voltages more easily than DC servo motors.2. Application
AC servo motors include an encoder that is used by the controller to provide feedback and closed-loop control. AC motors can be positioned with high precision and controlled precisely as required by the application. It is commonly used in robotics, automation, CNC equipment, speed controllers, water heaters, pumps, ovens, lawn mowers, air conditioners and many more applications.Difference between AC Servo Motor and DC Servo Motor
1. Principle: The DC servo motor is powered by a DC power supply, and the speed and direction of the motor are controlled by changing the magnetic field between the electrodes; The AC servo motor is powered by an AC power supply, and the speed and direction of the motor are controlled by changing the direction and magnitude of the current in the armature.
2. Speed regulation method: DC servo motors usually use PWM controllers to achieve speed regulation, while AC servo motors usually use vector controllers or vector inverters to achieve speed regulation
3. Controller: The controller of AC servo motor usually uses PLC or PID controller, which can realize closed-loop control, so that the motor can achieve higher precision; while the controller of DC servo motor generally uses PWM or analog controller, and the control method is relatively simple.
4. Maintenance & maintenance: AC servo motors have longer brush life and no commutator, so less maintenance is required; DC servo motors require frequent maintenance due to the existence of commutators and brushes.
5. Stability: AC servo motor has relatively high control precision, fast response speed, and better stability than DC servo motor; while DC servo motor has relatively low control precision and response speed, and relatively high stability Difference.
6. Speed & Torque: AC servo motor can generate high torque, so it is suitable for high torque and high speed working conditions. DC servo motors, on the other hand, have limited torque. So it adapts to the working condition of limited torque and speed.
7. Noise & operation: The AC servo motor runs smoothly and smoothly, with low noise, and there is no electronic (radio frequency) noise problem. In DC servo motors, the presence of brushes causes electronic (radio frequency) noise. Moreover, the DC servo motor is unstable and noisy
8. Weight & size: AC servo motors are relatively light in weight and small in size. DC servo motors are bulky and heavy.
9. Practical applications: AC servo motors are used in applications such as robots, machine tools, semiconductor equipment, and aircraft. The application fields of DC servo motors include computers, prime movers, controlled machinery, etc.
Advantages and disadvantages of AC servo motor and DC servo motor
(1) Advantages and disadvantages of AC servo motor
Advantages: good speed control characteristics, smooth control can be achieved in the entire speed range, almost no oscillation. High-speed control, high-precision position control (depending on the accuracy of the encoder), stable operation, good controllability, fast response, high sensitivity, and strict non-linearity indicators of mechanical characteristics and adjustment characteristics. In the rated operating area, it can realize constant torque, low inertia, low noise, no brush wear, and maintenance-free. Disadvantages: The control is more complicated, the drive parameters need to be adjusted on site to determine the PID parameters, and more connections are required.(2) Advantages and disadvantages of DC servo motor
Advantages: Accurate speed control, hard torque and speed characteristics, simple control principle, good linear adjustment characteristics, fast time response, easy to use, and cheap. Disadvantages: brush commutation, speed limitation, additional resistance, and wear particles (not suitable for dust-free and explosive environments). Therefore, when selecting a servo motor, it is necessary to comprehensively consider the actual application scenarios and requirements in order to select the most suitable type.