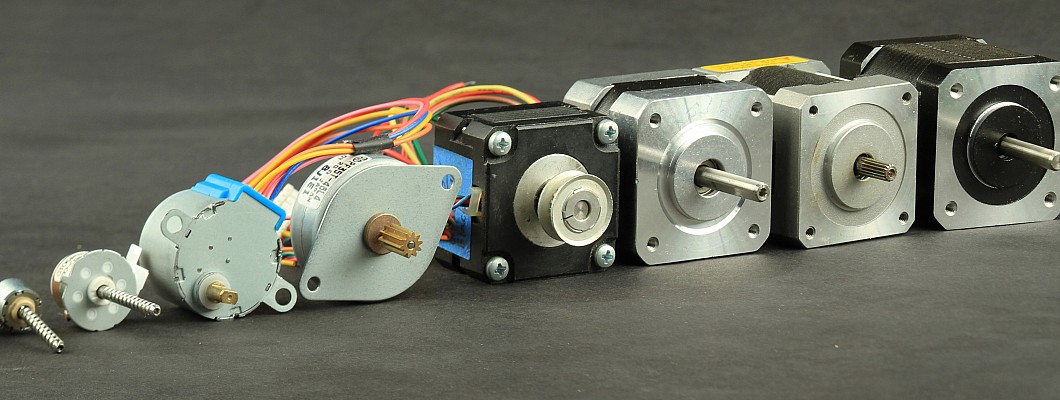
Stepper motors are widely used in many fields, so what factors should users pay attention to when facing a variety of stepper motors? This blog provides you with the following reference factors. Hope it can help you avoid some troubles caused by improper selection.
1. Torque of stepper motor
The holding torque of a stepper motor is similar to what is called "power" by a conventional motor. Of course, there are essential differences. The physical structure of the stepper motor is completely different from AC and DC motors, and the output power of the motor is variable. The type of motor is usually selected according to the required torque (that is, the torque required to drive the object). Generally speaking, if the torque is below 0.8N.m, choose 20, 28, 35, 39, 42 (the diameter or squareness of the motor body, unit: mm); if the torque is around 1N.m, choose 57 motors. When the torque is several N.m or greater, stepper motors with specifications of 86, 110, 130, etc. should be selected.
2. Speed of stepper motor
Special consideration should also be given to the speed of the motor. Because the output torque of the motor is inversely proportional to the speed. That is to say, the output torque of the stepper motor is large at low speed (hundreds of revolutions per minute or lower), and its output torque is very small at high speed rotation (1000 revolutions per minute - 9000 revolutions). . Of course, some working conditions require high-speed motors, and it is necessary to measure the coil resistance and inductance of the stepping motor to select a motor with a smaller inductance and a larger phase current, because as a high-speed motor, a larger output torque can be obtained . Conversely, when low speed and high torque are required, it is better to choose an inductance of more than ten or tens of mH, and a larger resistance.
3. No-load starting frequency of stepper motor
No-load starting frequency of stepping motor, usually called "no-load starting frequency". This is an important indicator for choosing a motor. If you require the motor to start and stop frequently in an instant, and its speed is around 1000 rpm (or higher), usually "accelerated start" is required. If you need direct start to achieve high speed, you are better off with a reactive motor or a permanent magnet motor. Because the "no-load starting frequency" of these motors is relatively high.
4. The number of phases of the stepper motor
Motors with different phase numbers have different working effects. The more the number of phases, the smaller the step angle can be made, and the vibration of the motor during working process is relatively small. In most occasions, two-phase motors are used more. In the working environment of high speed and high torque, it is more practical to choose a three-phase stepping motor.
5. Working environment
According to the environment in which the stepper motor is used, a special stepper motor with special functions such as waterproof, oilproof and shockproof should be selected for some special occasions. For example, underwater robots need waterproof motors. For motors used for special purposes, it is necessary to select motors with special functions.
6. Motor operating speed range
The speed range of the stepper motor is generally used within 600RPM, and the stepper motor has a torque-frequency characteristic. The output torque of the motor at a running speed of 600RPM is about 40% of the rated torque of the motor (the user can increase the power supply appropriately. voltage improves the output torque of the motor at high speed). When selecting the output torque of the motor, a certain safety margin should be considered to avoid the occurrence of lost step faults during the operation of the motor.
7. Motor installation size
The installation dimensions of the motor include: the installation flange size of the motor, the body size, the output shaft size and the output shaft type (optical shaft, platform shaft and shaft with key).
8. Control accuracy
If the accuracy requirement is relatively high, the stepper motor with encoder is preferred, that is, the closed-loop stepper motor.
9. Conventional driving method of stepper motor
It can be divided into constant voltage drive and constant current drive, unipolar drive and bipolar drive. Constant voltage drive refers to a constant drive voltage, which needs to be matched with a suitable resistance value, while constant current drive is usually aimed at motors with small resistance. The unipolar drive and bipolar drive are mainly due to the difference in the number of power tubes in the drive circuit, and the direction of the coil current in the coil is different.
10. If necessary, it is best to further communicate and confirm the model with the technical engineer of the manufacturer
If necessary, it is best to communicate further with the technical engineer of the manufacturer, so as to confirm whether the stepper motor you want to choose can meet all the indicators you require.
All in all, the above factors need to be considered when purchasing a stepper motor. In addition, it is recommended that you pay attention to whether the stepper motor has good waterproof, oil-proof and anti-corrosion performance when choosing, so that it can be better applicable to special products. Occasions, and if you need to use a stepper motor with special specifications, it is recommended to discuss with the manufacturer about custom-made matters.